Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to be widely adopted around the world. It can be sent securely and directly between people using Bitcoin’s network.
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto, who wrote a white paper describing the technology, created Bitcoin under a pseudonym. Digital money uses peer-to-peer technology to facilitate secure online peer-to-peer transactions.
- While other payment systems, such as Venmo and PayPal, require permission to transfer money from the traditional financial system, as well as existing debit or credit accounts, Bitcoin is decentralized: anyone in the world can send bitcoin to another without any involvement from a bank, government, or other institution.
- In Bitcoin, each transaction is tracked on the blockchain, which is similar to a bank’s ledger, which records customer funds entering and leaving. An audit trail records every bitcoin transaction that’s ever been made.
- Unlike bank ledgers, blockchains are distributed across a network of computers. Anyone can join that network; no country, company, or third party controls it.
- The number of Bitcoins will never exceed 21 million. Inflation and manipulation are impossible with this digital money.
- All you need is a fraction of a Bitcoin, you don’t need to buy an entire one. Bitcoin can be split into 1/100,000,000 units. This unit is called a Satoshi.
What Makes Bitcoin Special?
Bitcoin is an immutable and permissionless blockchain protocol. This means it can not be changed over time and there is no governing authority of this system. When there is a governing body incharge of a currency, the rules tend to be altered over time to favor this governing body. We typically see this play out in the form of inflation.
One example of how this negatively affects the world is seen in the longevity of modern day wars. In history when gold was the standard currency, countries who ran out of gold to pay for their war efforts were forced to surrender and end the war. Today, wars can go on for years funded by a never ending currency supply. The people who become victims of inflation are sadly those who seem to be doing the smart thing by saving their money. As inflation goes on, the money people save becomes devalued.
The Basics of Bitcoin
There have been thousands of cryptocurrencies launched since Bitcoin was created, but Bitcoin (abbreviated as BTC) continues to be the most valuable by market capitalization and trading volume. A key difference between Bitcoin and other crypto is the fact that it truly has no governing entity. Most others have a core group of developers who maintain control of the rules governing their tokens. Despite this, they still call their tokens “decentralized”.
- You can use Bitcoin in a variety of ways, depending on your goals. Some examples are as a means of investing, using it as a store of value, a global method of transferring value, or just to explore new emerging technologies.
- In the Internet age, Bitcoin has become a native currency. Bitcoin allows online transfers without involving middlemen such as banks or payment processors. This is one key difference from government-issued currencies such as the dollar or euro. In addition to allowing money to move more quickly and cheaply around the global internet, removing these gatekeepers provides individuals with the maximum level of control over their assets.
- While we encourage you to hold on to your Bitcoin over a long period of time, you can also use Bitcoin to make charitable donations, travel, and trade it. Many businesses accept it as a form of payment, including Whole Foods, Microsoft, and Home Depot.
- Does Bitcoin have value? All of these properties, as well as the fact that it is a medium of exchange and a store of value, make it a type of money. A physical version of it does not exist. It exists only digitally.
- Where does Bitcoin’s value come from? Similar to gold, it requires both energy and specialized equipment to create or mine Bitcoin. This equipment and energy is what provides work to secure transactions from one person to another.
Who is Satoshi Nakomoto?
To truly understand bitcoin, it’s helpful to start at the beginning. While journalists and members of the crypto community have dug deep into the origins of bitcoin, its creator remains anonymous a decade after it was invented.
- Satoshi Nakamoto, a person or group who goes by the name Satoshi, published a white paper online in late 2008 explaining the principles of bitcoin.
- Digital money was not the first concept to be drawn from the fields of cryptography and computer science—in fact, the paper references earlier concepts—but it offered an elegant solution to the problem of establishing trust between various online entities that are unable to locate themselves physically on the other side of the planet or who are hidden by pseudonyms (such as bitcoin’s own creator).
- Cryptocurrency and blockchain ledger are two interconnected concepts devised by Nakamoto. It is your private key that controls your bitcoin – a series of randomized numbers and letters that unlock a virtual vault containing the money you purchased. Using a virtual ledger called the blockchain, private keys are tracked.
It was a significant advance for computer science when Bitcoin first appeared since it dealt with a fundamental problem in online commerce: how does value get transferred between two people without the need for a trusted intermediary (such as a bank) to do so? With bitcoin, that problem has been solved, and its implications are far-reaching: A currency designed for the internet, it is a means of facilitating cross-border and global financial transactions without involving banks, credit card companies, lenders, or governments. It creates the potential for a more efficient, free, and innovative financial system when any two people can send payments to each other without encountering these gatekeepers. Basically, that’s bitcoin explained.
How does the Bitcoin Network Work?
There is no company or individual that owns bitcoin, unlike credit card networks and payment processors such as Paypal. With Bitcoin, anyone with an internet connection can participate in the first completely open payment network in the world. The underlying technology of Bitcoin enables it to be used on the internet without the need for banks or private companies to facilitate transactions.
The blockchain, a similar feature to a bank’s asset management system, is one of Bitcoin’s defining characteristics. Decentralized, meaning anyone can view the Bitcoin blockchain, and no single entity controls it, makes it different from a bank’s ledger.
Detailed information about how it all works can be found here:
- The equations necessary for verifying and recording new transactions are performed by specialized computers called mining rigs. Back then, almost anyone interested in mining was able to participate with a desktop PC that was powerful enough. The computers used today are massive, specialized, and are usually owned by businesses or large groups of people pooling their resources. (Mining a bitcoin in October 2019 requires 12 trillion times as much computing power as mining the first block did in January 2009.)
- The ever-growing ledger is kept accurate by the miners’ collective computing power. Whenever a new bitcoin is created or a transaction is made with any of the existing coins, it is recorded on the blockchain.
- What motivates miners to maintain the blockchain by verifying transactions constantly? Each mining rig in the Bitcoin network competes to be the first to solve a math problem. The Bitcoin ledger is updated every few minutes when a new winner is found. In early 2020, each winner of this raffle received 12.5 bitcoins.
- The value of a bitcoin was theoretically zero at the beginning. A price of around $7,500 was recorded at the end of 2019. As bitcoin’s value has increased, its easy divisibility (the ability to purchase fractions of one bitcoin) has become increasingly important. The bitcoin community refers to the smallest unit of bitcoin as a ‘Satoshi’. Bitcoin has an eight-decimal decimal place divisibility.
- Nakamoto designed the network in such a way that there would never be more than 21 million bitcoins, ensuring scarcity. The number of bitcoins available to be mined is currently around 3 million, which will decrease over time. Approximately 2140 will be the year that the last blocks are mined.
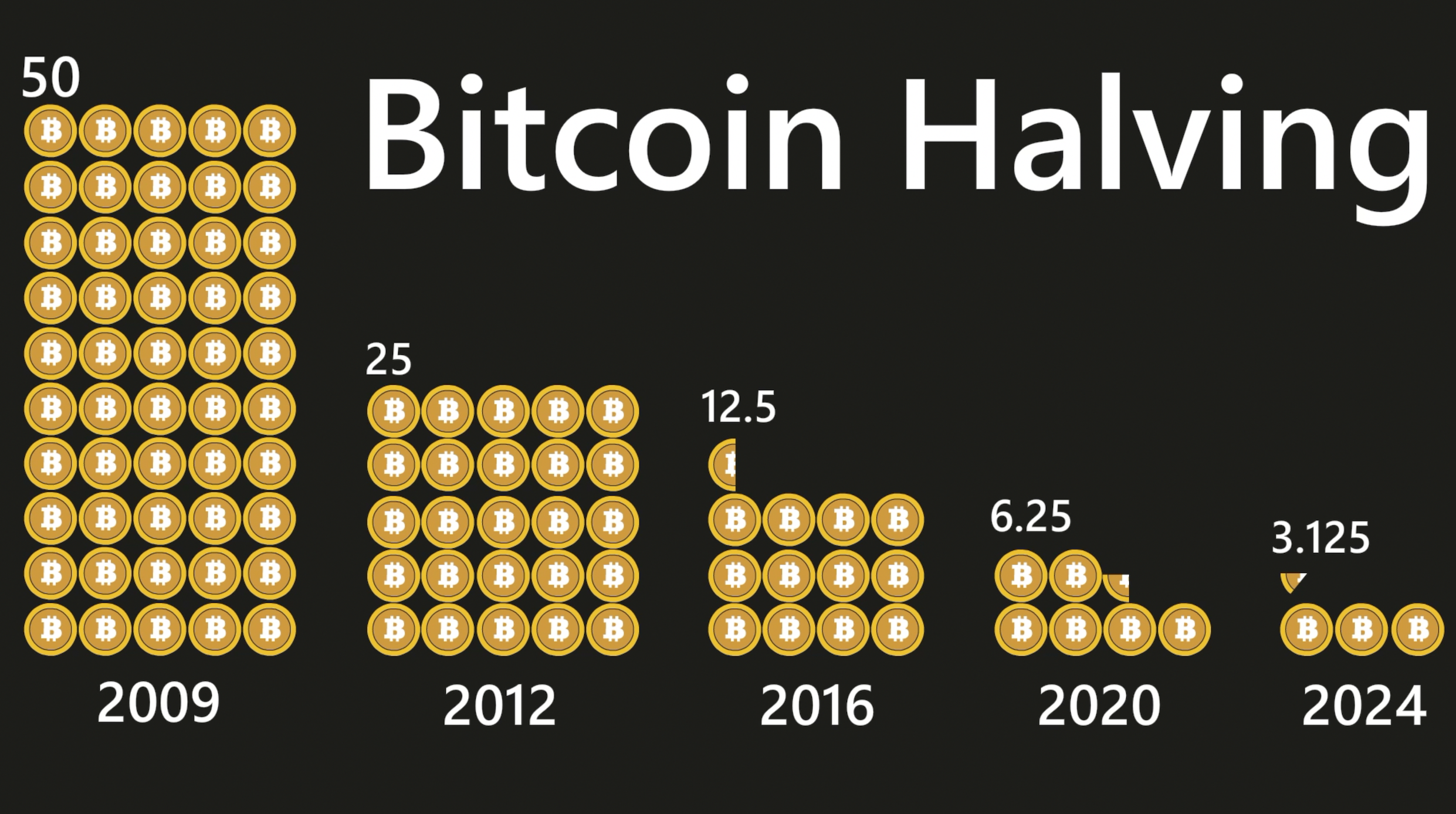
Why is Bitcoin Valuable
As with traditional currency, it’s been proven to be a viable and convenient means of storing value for many years. Consequently, it is readily exchangeable for goods, services, and other assets. Due to its scarcity, security, portability (as opposed to gold, for example), and easy divisibility, Bitcoin can be used for all kinds of transactions.
How Bitcoin works outside of an exchange
- A Bitcoin user receives a private key and a public key. A public key is similar to an email address, while a private key is similar to a password.
- You get a public key when you buy or send bitcoin, which is like unlocking a virtual vault and gaining access to your money when you do so.
- Using your public key, anyone can send you bitcoin, but only you can access them once they’re in the “virtual vault.”
- Bitcoin can be stored online or offline in a variety of ways.
What’s the difference between Bitcoin and Blockchain?
Blockchain is a virtual ledger that records all bitcoin transactions and public keys. Transactions are recorded chronologically in the ledger. Using enormous computing power across the globe, each bitcoin ledger is constantly checked and secured across all computers connected to the bitcoin network. In addition to cryptocurrencies, blockchains are now being used for things like supply-chain management, which has proven to be powerful and adaptable. Cryptocurrency blockchains store bitcoin transactions and private keys, and are referred to as ‘Bitcoin Blockchains’.
How is Bitcoin different from other forms of money?
There is no border to Bitcoin. Cash can be sent around the world as easily as cash can be sent in the real world. Weekends aren’t closed, you won’t be charged a fee to access your money, and there aren’t any arbitrary fees.
A bitcoin transaction cannot be reversed. The sender of Bitcoin cannot reverse transactions, like cash. Because of centralized intermediaries that complete transactions, credit cards, conventional online payment systems, and banking transactions can sometimes be reverted months after the payment has been made. Using credit cards is therefore more expensive for merchants because of the higher fraud risk.
Private transactions are possible with Bitcoin. The merchant does not need to receive bank statements or any unnecessary personal information when you pay with bitcoin. The bitcoin addresses and amounts involved in transactions are the only identifying information.
Bitcoin allows for secure transactions. Payments using Bitcoin are fundamentally more secure than those involving debit/credit cards because of the cryptographic nature of the network. Making bitcoin payments does not require sending sensitive information over the internet. Financial information or your identity is very unlikely to be compromised.
Bitcoin is an open currency. There is no exception to the public publication of every transaction on the Bitcoin network. Hence, transactions cannot be manipulated (except in a highly unlikely scenario of a 51% attack) and bitcoin’s supply can’t be changed. Software composing Bitcoin’s core is available to anyone as a free and open-source project.
It is safe to use Bitcoin. It has never been possible to successfully hack into the Bitcoin network in its ten years of existence. In addition, the system’s permissionless nature and open-source nature have allowed cryptographers and computer scientists to examine the security and efficiency of the system from every angle.
How is Bitcoin Made?
It is virtually ‘mined’ by an enormous network of decentralized computers known as peer-to-peer (also known as peer-to-peer networks) that constantly verify and secure the blockchain’s accuracy. The ledger reflects each and every bitcoin transaction, and new information is periodically added to previous blocks to form a new block.
If you enjoyed this article and would like to support this site
“Bitcoin will change us more than we change it”
-Marty Bent
“Every informed person needs to know about Bitcoin because it might be one of the world’s most important developments.”
— Leon Luow, Nobel Peace Prize nominee
Related Articles
Henry Ford’s Financial Vision and Nikola Tesla’s Machine Intelligence: The Convergence in Bitcoin
Introduction The dawn of the 20th century witnessed groundbreaking strides in industrial and technological advancements, primarily led by Henry Ford in manufacturing and Nikola Tesla in electrical engineering. While Ford revolutionized the automotive industry with his...
The Genesis of Bitcoin: Revolutionizing Digital Currency
Introduction: Bitcoin has emerged as a groundbreaking digital currency, reshaping our understanding of financial transactions in the digital age. Its creation by the enigmatic figure Satoshi Nakamoto marks a pivotal moment in the quest for a decentralized currency....
Henry Ford
Henry Ford: Henry Ford, the revolutionary industrialist who founded the Ford Motor Company and fathered modern assembly lines, was also a critical thinker when it came to the economic systems of his time. He was famously critical of the centralized banking system,...
Stay Up to Date With The Latest News & Updates
Access Premium Content
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque
Join Our Newsletter
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque
Follow Us
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque